eating disorders
WHAT IS a eating disorder?
There is a commonly held view that eating disorders are a lifestyle choice. Eating disorders are actually serious and often fatal illnesses that cause severe disturbances to a person’s eating behaviors. Obsessions with food, body weight, and shape may also signal an eating disorder. Common eating disorders include anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder.
signs & syMPTOMS
Anorexia nervosa
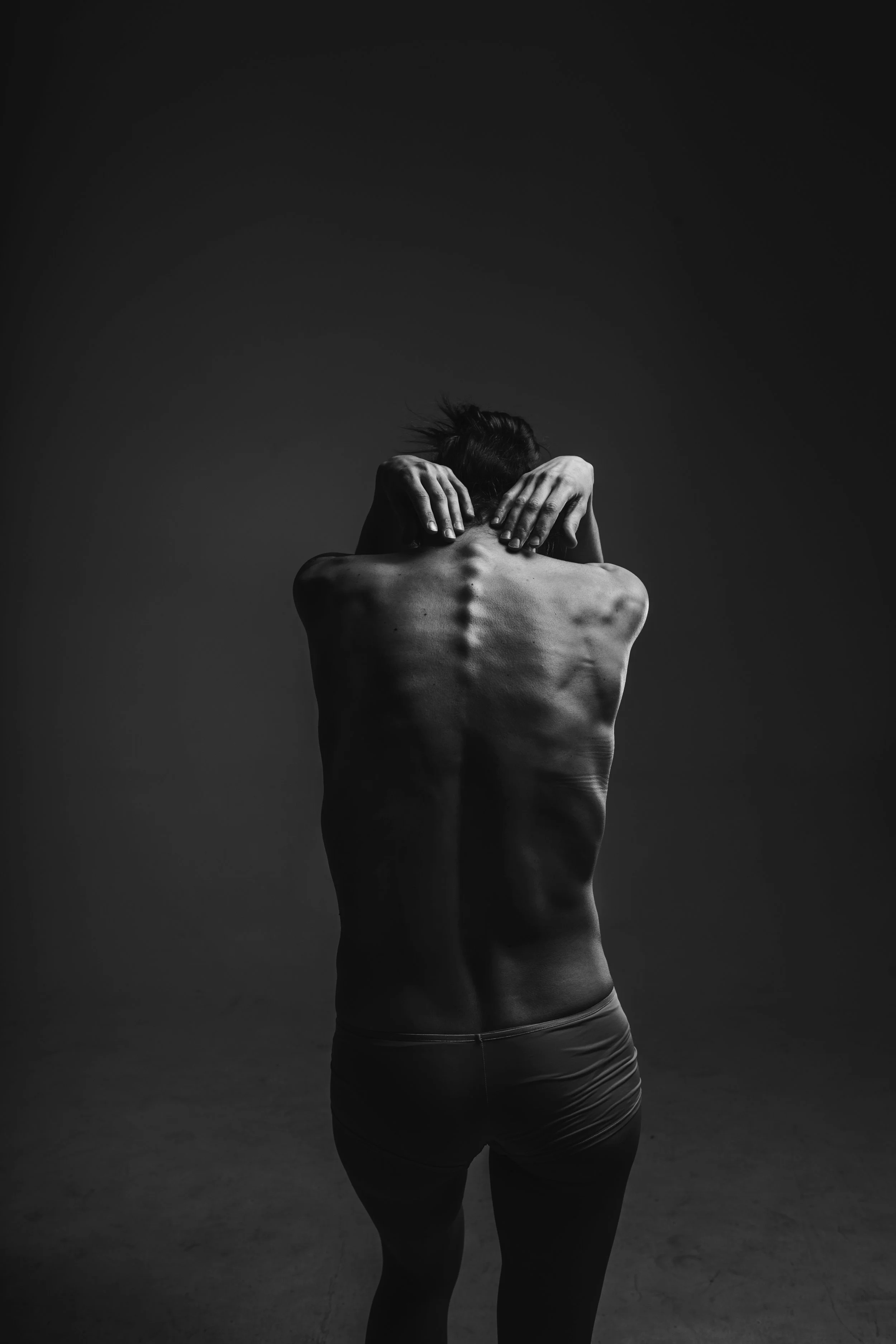
People with anorexia nervosa may see themselves as overweight, even when they are dangerously underweight. People with anorexia nervosa typically weigh themselves repeatedly, severely restrict the amount of food they eat, and eat very small quantities of only certain foods. Anorexia nervosa has the highest mortality rate of any mental disorder. While many young women and men with this disorder die from complications associated with starvation, others die of suicide. In women, suicide is much more common in those with anorexia than with most other mental disorders.
Symptoms include:
Extremely restricted eating
Extreme thinness (emaciation)
A relentless pursuit of thinness and unwillingness to maintain a normal or healthy weight
Intense fear of gaining weight
Distorted body image, a self-esteem that is heavily influenced by perceptions of body weight and shape, or a denial of the seriousness of low body weight
Other symptoms may develop over time, including:
Thinning of the bones (osteopenia or osteoporosis)
Mild anemia and muscle wasting and weakness
Brittle hair and nails
Dry and yellowish skin
Growth of fine hair all over the body (lanugo)
Severe constipation
Low blood pressure, slowed breathing and pulse
Damage to the structure and function of the heart
Brain damage
Multiorgan failure
Drop in internal body temperature, causing a person to feel cold all the time
Lethargy, sluggishness, or feeling tired all the time
Infertility
Bulimia nervosa
People with bulimia nervosa have recurrent and frequent episodes of eating unusually large amounts of food and feeling a lack of control over these episodes. This binge-eating is followed by behavior that compensates for the overeating such as forced vomiting, excessive use of laxatives or diuretics, fasting, excessive exercise, or a combination of these behaviors. Unlike anorexia nervosa, people with bulimia nervosa usually maintain what is considered a healthy or relatively normal weight.
Symptoms include:
Chronically inflamed and sore throat
Swollen salivary glands in the neck and jaw area
Worn tooth enamel and increasingly sensitive and decaying teeth as a result of exposure to stomach acid
Acid reflux disorder and other gastrointestinal problems
Intestinal distress and irritation from laxative abuse
Severe dehydration from purging of fluids
Electrolyte imbalance (too low or too high levels of sodium, calcium, potassium and other minerals) which can lead to stroke or heart attack
Binge-eating disorder
People with binge-eating disorder lose control over his or her eating. Unlike bulimia nervosa, periods of binge-eating are not followed by purging, excessive exercise, or fasting. As a result, people with binge-eating disorder often are overweight or obese. Binge-eating disorder is the most common eating disorder in the U.S.
Symptoms include:
Eating unusually large amounts of food in a specific amount of time
Eating even when you're full or not hungry
Eating fast during binge episodes
Eating until you're uncomfortably full
Eating alone or in secret to avoid embarrassment
Feeling distressed, ashamed, or guilty about your eating
Frequently dieting, possibly without weight loss
risks
Eating disorders frequently appear during the teen years or young adulthood but may also develop during childhood or later in life. These disorders affect both genders, although rates among women are higher than among men. Like women who have eating disorders, men also have a distorted sense of body image. For example, men may have muscle dysmorphia, a type of disorder marked by an extreme concern with becoming more muscular.
Researchers are finding that eating disorders are caused by a complex interaction of genetic, biological, behavioral, psychological, and social factors. Researchers are using the latest technology and science to better understand eating disorders.
Treatment Options
Adequate nutrition, reducing excessive exercise, and stopping purging behaviors are the foundations of treatment. Treatment plans are tailored to individual needs and may include one or more of the following:
Individual, group, and/or family psychotherapy
Medical care and monitoring
Nutritional counseling
Medications
Psychotherapies
Psychotherapies such as a family-based therapy called the Maudsley approach, where parents of adolescents with anorexia nervosa assume responsibility for feeding their child, appear to be very effective in helping people gain weight and improve eating habits and moods.
To reduce or eliminate binge-eating and purging behaviors, people may undergo cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), which is another type of psychotherapy that helps a person learn how to identify distorted or unhelpful thinking patterns and recognize and change inaccurate beliefs.
Medications
Evidence also suggests that medications such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, or mood stabilizers approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) may also be helpful for treating eating disorders and other co-occurring illnesses such as anxiety or depression. Check the FDA’s website: (http://www.fda.gov/), for the latest information on warnings, patient medication guides, or newly approved medications.